Conventional natural gas and renewable natural gas (RNG) might seem like interchangeable options for our energy needs. But a closer look reveals a key difference: their origin story. This article dives into how each fuel is formed and the environmental impact it carries. We’ll then explore their shared characteristics and the existing infrastructure that allows RNG to seamlessly integrate into our energy grid.
Key Differences of RNG & Conventional Natural Gas
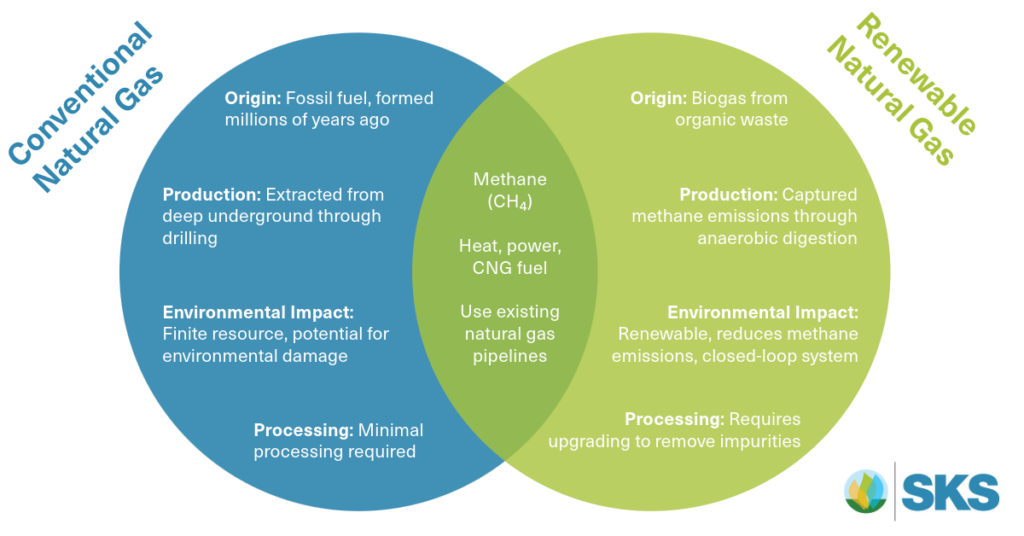
While both RNG and conventional natural gas can be used for fueling vehicles and generating heat and power, crucial differences lie in their origin, environmental impact, and processing pathways.
Origin
Conventional Natural Gas is a finite fossil fuel formed from the decomposed remains of organic matter buried deep underground millions of years ago. Extracting this gas requires deep well drilling, raising concerns about resource depletion and potential environmental damage.
RNG is a clean-burning fuel produced through a process called anaerobic digestion. This process captures methane emissions from organic waste sources like manure, food scraps, and wastewater treatment plants, utilizing the captured methane as a valuable energy source. By capturing these emissions, RNG facilities prevent them from entering the atmosphere as a potent greenhouse gas. In essence, RNG creates a closed-loop system that effectively recycles existing carbon.
Environmental Impact
The extraction and transportation of conventional natural gas can have negative environmental impacts. These concerns include methane leakage during extraction and transport, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, and potential contamination of water resources during the drilling process.
RNG offers a significant environmental benefit by capturing methane emissions from organic waste that would otherwise escape into the atmosphere. This captured methane is then converted into a clean-burning fuel source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and their associated environmental impacts.
Processing Pathways
While the exact processing steps can vary, conventional natural gas typically requires minimal processing due to its naturally high methane content (above 90%). Extracted wellhead gas (wet gas) may undergo separation to remove impurities like water vapor and sulfur compounds that could cause issues during transport or use. However, this processing is often minimal, and in some cases, the gas may be dry enough to avoid processing altogether.
In contrast, the initial output from the anaerobic digestion process, called raw biogas, requires additional processing called biogas upgrading. This crucial step removes impurities like carbon dioxide and trace gasses, concentrating the methane content to 95-99% through methods such as pressure swing adsorption, membrane separation, or cryogenic separation. Once upgraded, RNG becomes virtually indistinguishable from pipeline-quality natural gas.
Key Similarities of RNG & Conventional Natural Gas
Despite their contrasting origins, RNG and conventional natural gas share key characteristics that enable compatibility and offer advantages. Let’s explore these similarities in more detail.
Primary Component
Both RNG and conventional natural gas consist primarily of methane (CH₄). This shared composition allows for their interchangeable use in many applications. After undergoing the biogas upgrading process, RNG reaches a methane content of 95-99%, making it virtually indistinguishable from conventional natural gas in terms of its primary energy source.
End Uses
Both RNG and conventional natural gas offer versatility, providing heat and power for various applications, including:
- Heating Buildings: Homes, businesses, and industrial facilities can utilize both RNG and conventional natural gas to generate heat.
- Power Generation: Electricity can be produced in power plants by burning either RNG or conventional natural gas.
- Transportation Fuel: Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) vehicles can run on both RNG and conventionally sourced natural gas, offering a cleaner alternative to gasoline or diesel.
Existing Infrastructure
A significant advantage of RNG is its ability to leverage the existing natural gas pipeline network. Because upgraded RNG is nearly identical to conventional natural gas in composition, it can be injected directly into these pipelines. This eliminates the need for a separate infrastructure for RNG transportation, significantly reducing the cost and complexity of delivering this renewable fuel to consumers. This shared infrastructure allows RNG to be readily available and seamlessly integrated into the current energy system.
The Road to Renewable Gas Production
While both conventional natural gas and RNG address our energy needs, RNG emerges as a clear path towards a sustainable future. By capturing methane emissions from waste and transforming them into a clean-burning fuel, RNG tackles the twin challenges of resource depletion and greenhouse gas emissions associated with conventional gas. Additionally, the existing natural gas infrastructure readily accepts RNG, making it a practical and readily available solution.
For those considering the development of a biogas facility, several key factors warrant careful consideration:
- Feedstock Availability: A reliable source of organic waste is crucial. Evaluate potential feedstocks in your area, such as agricultural waste, food scraps, or wastewater treatment plant effluent.
- Facility Requirements: Research the necessary infrastructure for anaerobic digestion and biogas upgrading. Biogas facility design depends on feedstock type and desired output volume.
- Financial Considerations: Explore available grants, incentives, and loan programs to support the development of renewable energy projects. The financial viability of your facility will depend on factors like feedstock costs, tipping fees, and RNG production volume.
- Regulatory Landscape: Become familiar with any local, state, or federal regulations governing biogas production and RNG injection into pipelines.
SKS Development stands as a leading provider of renewable energy solutions. Our team offers the knowledge and experience to guide you in building the biogas facility that perfectly aligns with your needs. We take the time to understand your specific requirements and develop a solution that meets both your operational and investment objectives.
To learn more about the potential benefits of RNG for your dairy farm or other operations, please reach out to the SKS team. We are here to answer your questions and help you embark on a path towards a more sustainable and profitable future.
